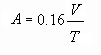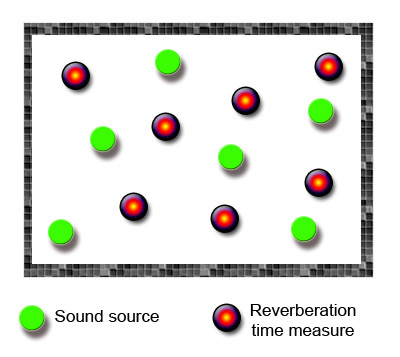
In a building's acoustic measurements the average reverberation time parameter is often referred to.
This average reverberation time is calculated from the average, frequency by frequency, of reverberation times measured in different room positions. Such measurements are repeated moving the sound source in various positions, according to form and dimension of the room tested.
The number of points considered depends on the tested room's form and dimensions.

The reverberation time T is defined as the time necessary for a 60dB sound level decay after interruption of the sound source in an enclosed space. Generally speaking, this measurement is not possible due to the insufficient signal/noise ratio of the source. Therefore the T20 and T30 estimations based on a decay respectively equal to 20dB and 30dB are calculated, starting from 5dB under the noise source maximum level.
For the reverberation time to have a meaning according to ISO norm, it is necessary that
the reference parameters were T20 or T30
the linear decay correlation coefficient were at least 0.95
the difference between signal level and background noise were at least 35 dB for T20 and 45 dB for T30
Equivalent absorption area
Another very frequently used parameter in architectonic acoustics for acoustically characterizing a room is the equivalent absorption area.
Given the average reverberation time T and the room volume V, the equivalent absorption area is calculated by the relation: